In the previous post, we set up the environment which provided us everything to start building Oracle APEX apps. In this post, I want to take the Oracle APEX apps I've built before and move them to this new service.
There are different ways of accomplishing this. Here are the steps I will follow:
- In the current environment
- Export the database (schema)
- Export the APEX app
- On the new Oracle APEX Application Development Service
- Import the database (schema)
- Import/Deploy the APEX app
I will start by moving a very small app I built a few years ago; the reservation of meeting rooms we use in the Innovation and Incubation center in which our office is located.
In our current environment, we will export the data and the APEX app as explained below.
Export the database schema
There are different ways to get your data: export to flat files, make your data available through REST web services or use some other tools to move data. We export all our apps every night to a different location with Oracle Data Pump. In case you are new to Data Pump, here's the command you can use to export a specific schema:
expdp apex_backup/xxx@apex_pdb directory=DATAPUMP dumpfile=db_20210121_ini.dmp logfile=db_20210121_ini.log schemas=INI exclude=statistics
or export the entire database:
expdp apex_backup/xxx@apex_pdb directory=DATAPUMP dumpfile=db_20210121_full.dmp logfile=db_20210121_full.log full=y exclude=statistics
I like to use Data Pump as it will export everything in one .dmp file and it's really fast to do.
Export the APEX application
There are different ways to export the APEX app. You can export through the GUI in Oracle APEX, use the external APEX Export tool, or use SQLcl.
Just like with the data, we also export all APEX workspaces and applications every night. We use the APEX Export tool. This is especially useful if you want to move your entire environment to the cloud as you don't have to export workspaces and apps one by one.
The command to export all workspaces:
/usr/bin/java oracle.apex.APEXExport -db localhost:1521/APEX_PDB -user apex_backup -password xxx -expWorkspace > workspaces.txt
The command to export all applications:
/usr/bin/java oracle.apex.APEXExport -db localhost:1521/APEX_PDB -user apex_backup -password xxx -instance > applications.txt
Now that we have the database data pump file (.dmp) and the APEX export file (.sql), we are ready to go to the new APEX Application Development Service to import the database and Oracle APEX app.
Import the database schema
The first thing we will do is import the database into the new service.
Log in to the Oracle Cloud and go to the APEX Application Development > APEX Instances.
From there click on the database link:
Here you arrive in the database. There's a DB Connection button:
First, we will make the dump file available to the Data Pump API. The database in the Oracle Cloud can not read a file from your filesystem directly, so you have to make the file available so the database can read it. In the Oracle Cloud, we can use Object Storage to store our dump file. In my blog post Setup Object Storage and use for File Share and Backups, you find step-by-step instructions both to upload through the GUI as from the command line.
As this is a very small database, I will just use the GUI. For anything that is less than 500MB you can most likely use the OCI Console, but for large data pumps the GUI will time out. In case your dump file is bigger, use the OCI REST API or CLI, or SDK.
Go to Object Storage :
Create a Bucket:
Make sure to copy the URL of the dump file. In order to do so, click the three dots next to the file and click View Object Details
First, I typically create the user with a script:
create user ini identified by Thisisrealsecure123;
grant connect to ini;
grant create job to ini;
grant create dimension to ini;
grant create indextype to ini;
grant create operator to ini;
grant create type to ini;
grant create materialized view to ini;
grant create trigger to ini;
grant create procedure to ini;
grant create sequence to ini;
grant create view to ini;
grant create synonym to ini;
grant create cluster to ini;
grant create table to ini;
grant create session to ini;
grant execute on ctxsys.ctx_ddl to ini;
grant execute on dbms_crypto to ini;
alter user ini quota unlimited on data;
Next, import the data pump file which we stored earlier in Object Storage.
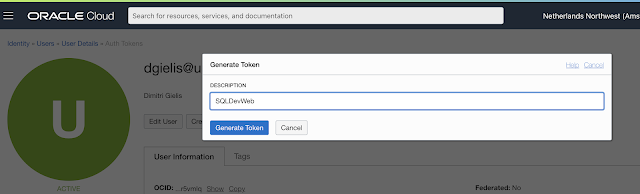
In order to connect to Object Storage from SQL Dev Web we need some Cloud Credentials. Just like in the first post where we created the SMTP credentials, we will now go to that screen to create some Auth Credentials.
Go to Identity > Users and select your user and click the Auth Tokens:
begin
dbms_cloud.create_credential(
credential_name => 'YourName',
username => 'YourUser',
password => 'YourPassword');
end;
/
In my case it looks like this:
begin
DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT(
credential_name => 'dgielis',
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.eu-amsterdam-1.oraclecloud.com/n/ax54uj3ardud/b/db_import/o/db_20210119_ini.dmp',
directory_name => 'DATA_PUMP_DIR');
end;
I took a screenshot of some more commands I used to check my environment:
- The first command to check I had credentials (dba_credentials)
- The second to query the Object Storage bucket
- The third to put the object from the Object Storage onto the database machine
- The fourth command to make sure the dump file was in the directory
declare
ind NUMBER; -- Loop index
h1 NUMBER; -- Data Pump job handle
percent_done NUMBER; -- Percentage of job complete
job_state VARCHAR2(30); -- To keep track of job state
le ku$_LogEntry; -- For WIP and error messages
js ku$_JobStatus; -- The job status from get_status
jd ku$_JobDesc; -- The job description from get_status
sts ku$_Status; -- The status object returned by get_status
begin
-- Create a Data Pump job to do a "full" import (everything in the dump file without filtering).
h1 := DBMS_DATAPUMP.OPEN('IMPORT','FULL',NULL,'INI');
-- Add the file to the job handler
DBMS_DATAPUMP.ADD_FILE(h1,'db_20210119_ini.dmp','DATA_PUMP_DIR');
-- As on the previous system the tablespace was different, I remap the tablespace
DBMS_DATAPUMP.METADATA_REMAP(h1,'REMAP_TABLESPACE','INI','DATA');
-- In case you migrate from a legacy Schema Service, in addition, to remap the
-- tablespace, you may also want to remap the schema to a more user-friendly name
--
DBMS_DATAPUMP.METADATA_REMAP(h1,'REMAP_SCHEMA','DBPTTTBDEG1JF','MYNEWSCHEMA');
-- Start the job. An exception is returned if something is not set up properly.
DBMS_DATAPUMP.START_JOB(h1);
-- The import job should now be running. In the following loop, the job is
-- monitored until it completes. In the meantime, progress information is displayed.
percent_done := 0;
job_state := 'UNDEFINED';
while (job_state != 'COMPLETED') and (job_state != 'STOPPED')
loop
dbms_datapump.get_status(h1,
dbms_datapump.ku$_status_job_error +
dbms_datapump.ku$_status_job_status +
dbms_datapump.ku$_status_wip,-1,job_state,sts);
js := sts.job_status;
-- If the percentage done changed, display the new value.
if js.percent_done != percent_done
then
dbms_output.put_line('*** Job percent done = ' || to_char(js.percent_done));
percent_done := js.percent_done;
end if;
-- If any work-in-progress (WIP) or Error messages were received for the job, display them.
if (bitand(sts.mask,dbms_datapump.ku$_status_wip) != 0)
then
le := sts.wip;
else
if (bitand(sts.mask,dbms_datapump.ku$_status_job_error) != 0)
then
le := sts.error;
else
le := null;
end if;
end if;
if le is not null
then
ind := le.FIRST;
while ind is not null loop
dbms_output.put_line(le(ind).LogText);
ind := le.NEXT(ind);
end loop;
end if;
end loop;
-- Indicate that the job finished and gracefully detach from it.
dbms_output.put_line('Job has completed');
dbms_output.put_line('Final job state = ' || job_state);
dbms_datapump.detach(h1);
end;
/
And here's the result, everything nicely imported:
When executing the import script in SQL Developer Web (SDW), for large imports, it is possible you will be timed out of SDW before the import job finishes. To monitor the status of the job, you can open another SDW instance and monitor the job.
declare
ind NUMBER; -- Loop index
h1 NUMBER; -- Data Pump job handle
percent_done NUMBER; -- Percentage of job complete
job_state VARCHAR2(30); -- To keep track of job state
le ku$_LogEntry; -- For WIP and error messages
js ku$_JobStatus; -- The job status from get_status
jd ku$_JobDesc; -- The job description from get_status
sts ku$_Status; -- The status object returned by get_status
begin
-- Attach to the Data Pump job
h1 := DBMS_DATAPUMP.ATTACH('IMPORT','INI');
-- Get the Job Status
dbms_datapump.get_status(h1,
dbms_datapump.ku$_status_job_error +
dbms_datapump.ku$_status_job_status +
dbms_datapump.ku$_status_wip,-1,job_state,sts);
js := sts.job_status;
-- check percent done and output to console
percent_done := js.percent_done;
dbms_output.put_line('*** Job percent done = ' || to_char(percent_done));
-- Detach
DBMS_DATAPUMP.DETACH(h1);
end;
In case the status is going bananas, here's a short script you can execute to kill the job if needed.
declare
ind NUMBER; -- Loop index
h1 NUMBER; -- Data Pump job handle
percent_done NUMBER; -- Percentage of job complete
job_state VARCHAR2(30); -- To keep track of job state
le ku$_LogEntry; -- For WIP and error messages
js ku$_JobStatus; -- The job status from get_status
jd ku$_JobDesc; -- The job description from get_status
sts ku$_Status; -- The status object returned by get_status
begin
-- Attach to the Data Pump job
h1 := DBMS_DATAPUMP.ATTACH('IMPORT','INI');
-- Stop the job
dbms_datapump.stop_job(h1, 1);
-- Detach
DBMS_DATAPUMP.DETACH(h1);
end;
Credit to Todd Bottger (update on 30-APR-2021):
-- //start
There are two different ways to get the actual import job done in PL/SQL. Each has tradeoffs.
1) Use of DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT followed by DBMS_DATAPUMP import from the local file as described above: this approach probably will be the fastest one for large data sets.
The downsides are slightly more complex script (more lines of script) and it consumes extra storage space due to GET_OBJECT making a full local copy first. Note that customers pay for this storage space as part of their storage bill. Of course, the price per TB in APEX Service is quite low, so perhaps it will not be a big concern for most folks.
2) Alternative approach using DBMS_DATAPUMP *only*.
Note that DBMS_DATAPUMP in ADB-S now supports importing directly from OCI Object Storage.
This was implemented in DB 21c and backported to DB 19c for internal patch applied to ADB-S services (including APEX service). Here and here are some DB 21c docs that cover it.
I have on good authority from folks here at Oracle that this operation reads data over the network and imports in real-time. There are some internal optimizations like read-ahead caching, but it does not make an additional copy to local disk, which is nice. This approach results in simpler script (fewer lines of code – no need for DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT) and also avoids consuming the extra storage space.
However, there are performance points to be aware of – i.e. network latencies and some overheads in object storage itself – that probably make it slower than Option A.
It still might be a good approach for when users want the simplest possible PL/SQL script and they are importing a small data set:
DBMS_DATAPUMP.ADD_FILE(h1, 'https://swiftobjectstorage.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com/v1/<objectstoragenamespace>/<bucketname>/<dumpfilename>', 'MYCREDENTIAL', NULL, dbms_datapump.ku$_file_type_uridump_file);
Side note: I believe you can use the <filename>_%U.dmp syntax at the end of such URLs when the export was split across multiple files like export_01.dmp, export_02.dmp, etc. to automatically import them all
-- //end
Now that we have our database (all objects and data), let's import the Oracle APEX app.
First, we have to create the workspace. I tried to find an easy way to run my workspace sql file, but couldn't. For example in SQL Developer on the desktop, I can just run files from a URL, but in SQL Dev Web this is not available yet:
So, I went with the conventional way of importing my APEX Workspace through APEX itself.
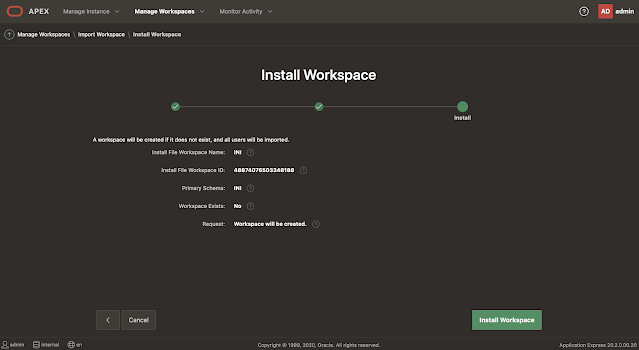
Log in to the INTERNAL workspace and click on Manage Workspace - Import Workspace:
Log in to the workspace we just imported. Note that you log in with the ADMIN user, same as INTERNAL:
Next up, import the APEX application. We could go to App Builder and follow the import wizard.
If you have only a handful of applications, this is definitely a good way. However, if you are moving hundreds of apps to this environment you probably more want to script it.
Here's a way you could do it. I uploaded the APEX app export files also to Object Storage.
In order to use this file in APEX, we create a Pre-Authenticated Request, so basically for a specific amount of time, we can access our file without the need for a password and other credentials.
declare
l_source apex_t_export_files;
begin
l_source := apex_t_export_files (
apex_t_export_file (
name => 'f263.sql',
contents => apex_web_service.make_rest_request (
p_url => 'https://objectstorage../f263.sql',
p_http_method => 'GET' )));
apex_application_install.install(p_source => l_source );
end;
And presto, the APEX app is installed:
There are probably more ways to do it, so feel free to comment on this blog post with an improved flow.
I also expect in the future it becomes easier. One of the focus points of Oracle APEX 21.1 and further is to make the integration with other Oracle Cloud services easier. If for example Object Storage was known by APEX_APPLICATION_INSTALL or other we would have fewer steps.
That's it for now, next up, configure printing and exporting.
Update 30-APR-2021:
Todd Bottger sent me a few commands which I incorporated in the blog post. Thank you, Todd!




































Brilliant Dimitri !. Thank you for showing the option of using Datapump from PL/SQL. This opens up the APEX service to a whole new segment of clients :-). I feared there where no easy way to migrate (other than insert scripts).
ReplyDeleteBrgds
Martin
What if the database we are moving is large - say 500 GB? Will these techniques work in a reasonable amount of time OR there are other techniques available possibly for an extra charge?
ReplyDeleteWill this method work for moving applications built on APEX 22 (via apex.oracle.com) to APEX21 development service on OCI. The conventional Apex import/export process keeps saying invalid export file in the OCI APEX development service.
ReplyDeleteapex.oracle.com is already on APEX 22.1, but OCI APEX is not yet on this release.
ReplyDeleteYou can only import to the same or a higher version of APEX.
Hope that clarifies.
Dimitri
Nice nice nice, all passed like a charm. Only thing that I had a problem is to connecto to WS. I have to create another user from internal to connect to my WS.
ReplyDeleteIs there some blog about implementing JRI. It would be great Job if You could make something like that.
Thank You
This was a nice post that helped me implement the same process through GITHUB.
ReplyDelete1. schema export and Apex application export to GITHUB
2. schema import and Apex application import from GITHUB
Advantage of using GITHUB is that is serves as a backup infrastructure that is independent of the OCI environment. I run the backup/restore process every night between 2 Always Free ADB databases, which gives some reassurance in case the databases are unexpectedly reclaimed.
Using this approach avoids complexity of Cloud storage, although it's only valid for relatively small files - i.e. <100MB files.
I was surprised that Application Static Files were imported - I thought that was something we still had to do manually.
Hi,
ReplyDeleteI have been writing earlier, in that time it was everything works fine with import schema, but today I got error when it comes to part with dbms_datapump.start_job(h1) and it says:
ORA-39002: invalid operation
ORA-06512: at "SYS.DBMS_DATAPUMP", line 7376
ORA-06512: at "SYS.DBMS_SYS_ERROR", line 79
ORA-06512: at "SYS.DBMS_DATAPUMP", line 4972
ORA-06512: at "SYS.DBMS_DATAPUMP", line 7370
ORA-06512: at line 26
Error at Line: 7 Column: 0
SO, can You pleas help with this error